
Sensitivity/pain in a tooth on having something cold especially drinking something chilled/cold. Pain in the tooth while applying pressure to eat/chew something (the patient avoids eating on the side where the infected tooth is). A pimple near the gum of the infected tooth which comes and goes (may or may not have pus); this tooth may or may not have pain.
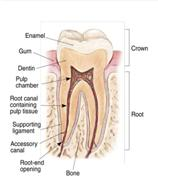
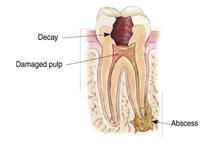
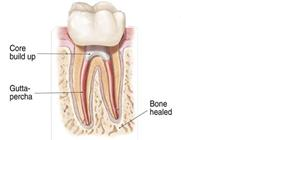
Tooth
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last teeth to appear in your mouth, occurring normally 17 and 25 years of age.When wisdom teeth are aligned properly and the gum tissue is healthy, they do not have to be removed. Unfortunately, this is not always the case. Extraction becomes necessary when they are prevented from properly growing in the mouth - they could grow sideways, partially emerge from the gums and even remain trapped beneath the gums and bone. Such impacted teeth can take many positions in the bone as they attempt to find a pathway that will allow them to grow.These poorly positioned impacted teeth can cause many problems - when they grow only partially, the opening around the tooth allows bacteria to grow and eventually causes an infection. The result: swelling, stiffness, pain and illness. The pressure from the growing wisdom tooth may move other teeth and disrupt the orthodontic or natural alignment of teeth. The most serious problem occurs when tumors or cysts form around the impacted wisdom tooth, resulting in the destruction of the jawbone and healthy teeth. Removal of the offending impacted tooth or teeth usually resolves these problems. Early removal is recommended to avoid such future problems and to decrease surgical risks involved with the procedure.
